PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
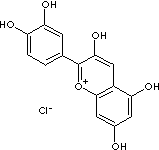
Anthocyanidin: Benzopyrylium (chromenylium) salts with chloride as the counterion. Not to be confused with Anthocyanin, their sugar containing counterparts. Anthocyanidins are sugar-free counterparts of anthocyanins, can be identified based on the structure of a large group of polymethine dye, the benzopyrylium (chromenylium) ion. In particular anthocyanidins are salt derivatives of the 2-phenylchromenylium cation also known as flavylium cation. As shown in the figure below, the phenyl group at the 2-position, can carry different substituents. The counterion of the flavylium cation is mostly chloride. With this positive charge the anthocyanins differ from other flavonoids.(http://www.neticasolution.com/)
Flavonoid is any member of a class of widely distributed biological natural products containing aromatic heterocyclic skeleton of flavan (2-Phenylbenzopyran) but no nitrogen in plants. Generally, flavonoids are biological pigments providing colours from red to blue in flowers, fruit and leaves. Besides their coloring in plants, flavonoids have important roles in the growth and development of plants; protection against UV-B radiation; forming antifungal barriers; antimicrobial, insecticidal and oestrogenic activities; plant reproduction. Flavonoids also exhibit a wide range of biological properties including anti-microbial, insecticidal and oestrogenic activities. Flavonoids are usually classified into main 6 subgroups as below plus flavans, neoflavonoids, flavonols, aurons, catechins according to the structural patterns.
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone): Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Apigeninidin, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin
|
|
ASSAY (HPLC)
90.0% min